Failover Service Management with AWS
In a failover, database volumes and licenses migration are usually covered by tools such as pacemaker. This project’s goal is to create a failover service that can automate execution of services not covered by 3rd party applications such as HVR and cron jobs. Two methods are presented in this writing. All testing is done on AWS.
A) Failover Management Service from Primary to Secondary with an Observer Server
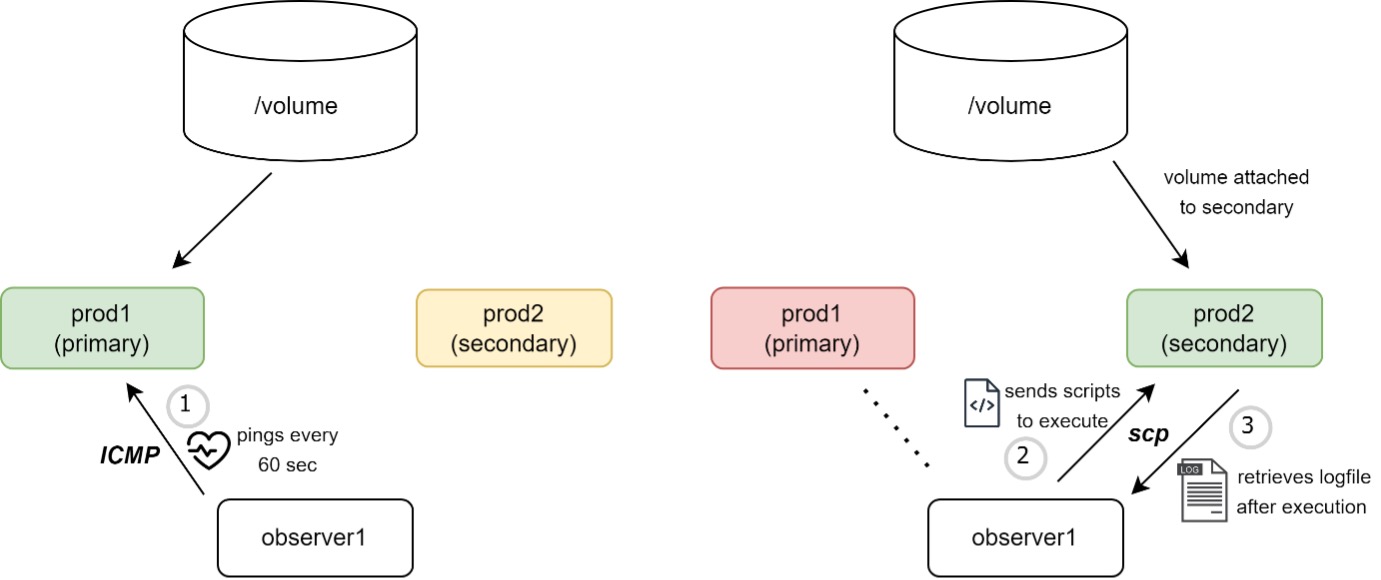
- A primary server (prod1) will have production volume (EBS in our case) attached to it.
- An observer server checks for the heartbeat of the primary server via ICMP protocol every 60 seconds.
- Manually stop the primary server (EC2 instance stop) to simulate server failure.
- The failover script kicks in by detaching the volume from the primary and attaching it to the secondary (ec2 attach-volume).
- A script is sent over from the observer to the secondary server. Inside the shell script are instructions to start both HVR and cron jobs.
- The logs from the secondary server are transferred back to the observer server via SCP protocol.
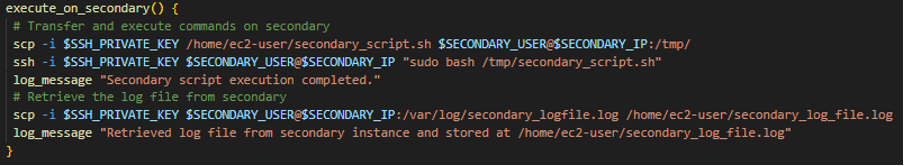
Here are some snapshots of the code involved in the transfer of the file to secondary:
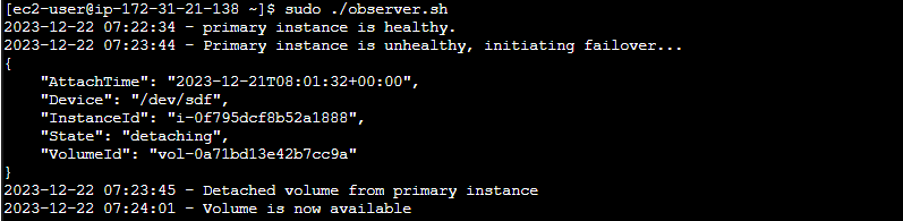
JSON Response for Detaching EBS
When you detach an EBS from an EC2 instance, it returns the following JSON:
B) Failover Management Service Without Observer
If we remove the need for an observer server, we then have a single script running in both servers. This script would continuously run in each server independently of one another. Here’s the logical flow of the script:
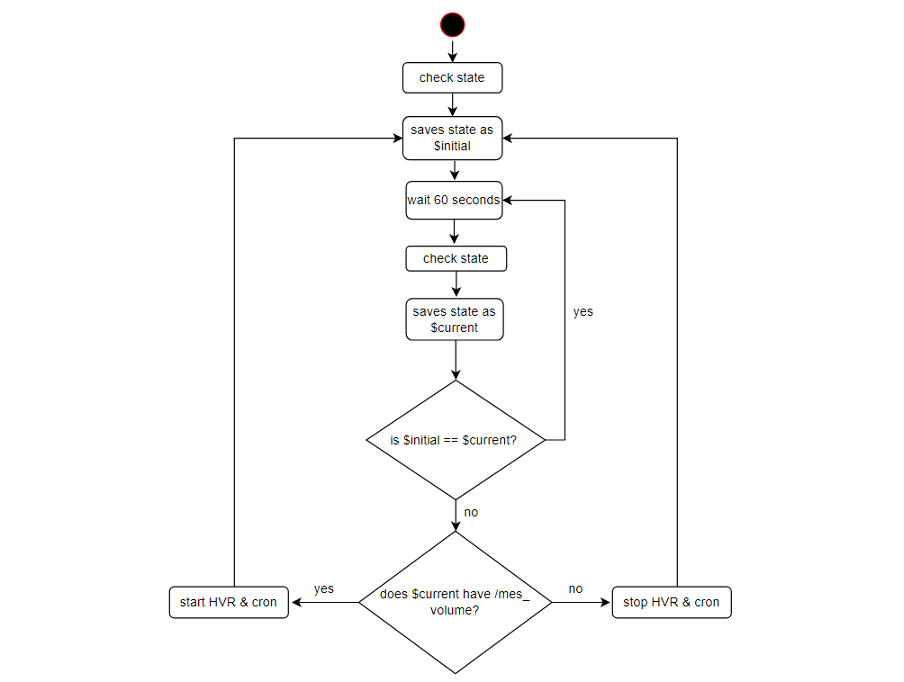
Since there is no observer server, the script is deployed onto both the primary and secondary (maintained via rsync).
We can simulate all the above in a single EC2 instance. Here’s the console output and the explanation for each step:
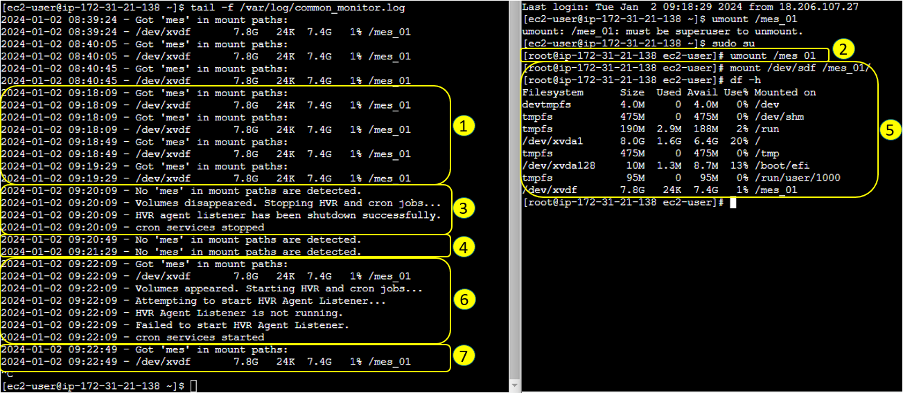
- Check the presence of MES (manufacturing execution system) volume.
- Unmount to simulate failure.
- HVR and cron services are stopped.
- Script continuously runs and now detects that no volume is attached.
- Mount back MES volume to simulate secondary server.
- Script detects MES volume appeared, initiates HVR and cron START.
- Volume is now present.
Closing Thoughts
This project started by creating a failover service management that administers code manually to the secondary server from an observer server. The project achieves its objective, but the overhead and manual administration is tedious and prone to failure. As a cloud user, I have grown to appreciate how convenient cloud platforms like AWS have made services and meeting user requirements so easy. Failover configurations and management can be easily done with a few button clicks with low code. Some of the AWS failover services include AWS Route 53, Auto Scaling Group, CloudFormation, Lambda and EventBridge.
This is my first blog post, if you have any thoughts, please feel free to contact me! Your feedback is appreciated.